How to Generate an SSH Key on macOS (Step-by-Step Guide)
Secure Shell (SSH) keys are an essential tool for developers, sysadmins and anyone managing code repositories. If you’re working with GitHub, Bitbucket or remote servers on a Mac in Australia, you’ll almost certainly need to generate and manage SSH keys. This article will walk you through the process of creating, configuring and testing SSH keys on macOS.
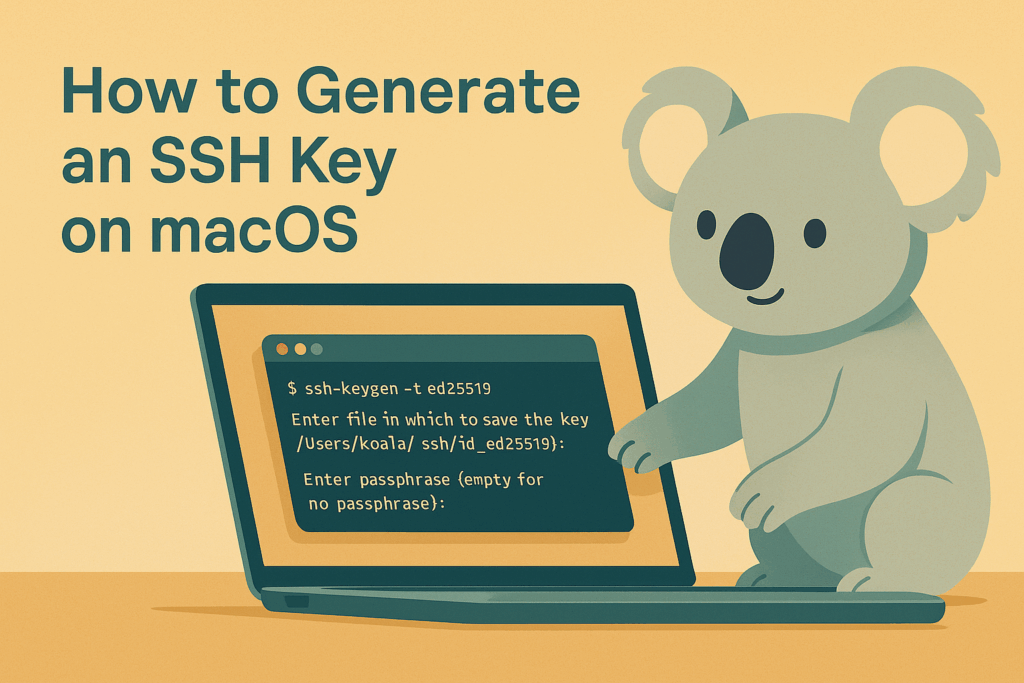
Table of Contents
- What is an SSH key?
- Prerequisites before generating SSH keys
- Step-by-step: Generate SSH key on macOS Terminal
- Where to find your SSH keys on macOS
- Adding SSH key to the macOS keychain
- Adding SSH key to GitHub on macOS
- Adding SSH key to Bitbucket on macOS
- Testing your SSH connection
- Troubleshooting common issues
- Best practices for managing SSH keys
- FAQ
What is an SSH key?
An SSH key is a cryptographic key pair (public and private) used to authenticate securely between your Mac and a remote server or service such as GitHub or Bitbucket. Unlike passwords, SSH keys provide stronger security and convenience, especially when working with repositories and automation.
Prerequisites before generating SSH keys
- Ensure you have macOS Terminal (pre-installed on all Macs).
- Make sure you have OpenSSH available (macOS includes it by default).
- Optional: A GitHub or Bitbucket account if you plan to use SSH for repositories.
Step-by-step: Generate SSH key on macOS Terminal
Open Terminal and run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "[email protected]"Explanation of options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-t ed25519 | Specifies the key type (modern and recommended). Use rsa if older systems require it. |
-C | Comment, usually your email for identification. |
You’ll be prompted to choose a file location (press Enter to accept the default) and optionally set a passphrase for extra security.
Where to find your SSH keys on macOS
SSH keys are stored in the ~/.ssh/ directory by default. Common files include:
id_ed25519(private key)id_ed25519.pub(public key)
Adding SSH key to the macOS keychain
To make your SSH key automatically available without retyping the passphrase:
ssh-add --apple-use-keychain ~/.ssh/id_ed25519Adding SSH key to GitHub on macOS
- Copy your public key:
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub - Go to GitHub > Settings > SSH and GPG keys.
- Click New SSH key, paste the key, and save.
Adding SSH key to Bitbucket on macOS
- Copy the public key (same as above).
- Go to Bitbucket > Personal settings > SSH keys.
- Add the key and confirm.
Testing your SSH connection
Test with GitHub:
ssh -T [email protected]Test with Bitbucket:
ssh -T [email protected]Troubleshooting common issues
- Permissions error: Run
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519. - SSH agent not running: Start it with
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)". - Wrong key type: Try generating with
-t rsaif older servers don’t support ED25519.
Best practices for managing SSH keys
- Use ED25519 unless compatibility requires RSA.
- Always protect private keys with correct file permissions.
- Consider using a passphrase for sensitive environments.
- Backup your keys securely but never share private keys.
- Use different keys for work and personal projects if possible.
Conclusion
Generating an SSH key on macOS is straightforward with Terminal. Once created, you can use the key for GitHub, Bitbucket and other secure connections. Following best practices ensures both convenience and security for Australian developers managing code and infrastructure.